A company's latest accounts show profit after tax of $20.0 million, after deducting interest of $5.0 million. The company expects earnings to grow at 5% per annum indefinitely.
The company has estimated its cost of equity at 12%, which is included in the company WACC of 10%.
Assuming that profit after tax is equivalent to cash flows, what is the value of the equity capital?
Give your answer to the nearest $ million.
$ ? million
Company B is an all equity financed company with a cost of equity of 10%.
It is considering issuing bonds in order to achieve a gearing level of 20% debt and 80% equity.
These bonds will pay a coupon rate of 5% and have an interest yield of 6%.
Company B pays corporate tax at the rate of 25%.
According to Modigliani and Miller's theory of capital structure with tax, what will be Company B's new cost of equity?
A)
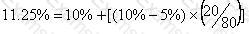
B)
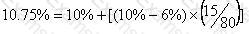
C)
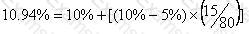
D)
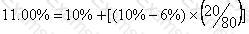
Option A
Option B
Option C
Option D
A private company manufactures goods for export, the goods are priced in foreign currency B$.
The company is partly owned by members of the founding family and partly by a venture capitalist who is helping to grow the business rapidly in preparation for a planned listing in three years' time.
The company therefore has significant long term exposure to the B$.
This exposure is hedged up to 24 months into the future based on highly probable forecast future revenue streams.
The company does not apply hedge accounting and this has led to high volatility in reported earnings.
Which of the following best explains why external consultants have recently advised the company to apply hedge accounting?
An all equity financed company plans an issue of new ordinary shares to the general public to raise finance for a new project
The following data applies:
• 10 million ordinary shares are currently in issue with a market value of S3 each share
• The new project will cost S2.88 million and is expected to give a positive NPV of S1 million
• The issue will be priced at a AaA discount to the current share price.
What gam or loss per share will accrue to the existing shareholders?
An entity prepares financial statements to 30 June.
During the year ended 30 June 20X2 the following events occurred:
1 July 20X1
• The entitiy borrowed $100 million at a variable rate of interest.
• In order to protect itself against the variability of its interest cashflows, the entity entered into a pay-fixed-receive-variable interest swap with annual settlements. The fair value of the swap on this date was zero.
30 June 20X2
• The entity received a net settlement of $2 million under the swap. After this net settlement, the fair value of the swap was $5 million - a financial asset.
The entity decides to use hedge accounting for this arrangement and has designated it as a cash flow hedge. The swap is a perfect hedge of the variability of the cash interest payments.
Which of the following describes the treatment of the settlement and the change in the fair value of the swap in the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income for the year ended 30 June 20X2?
ZZZ wishes to borrow at a floating rate and has been told that it can use swaps to reduce the effective interest rate it pays. ZZZ can borrow floating at the risk-free rate + 1, and fixed at 10%.
Which of the following companies would be the most appropriate for ZZZ to enter into a swap with?
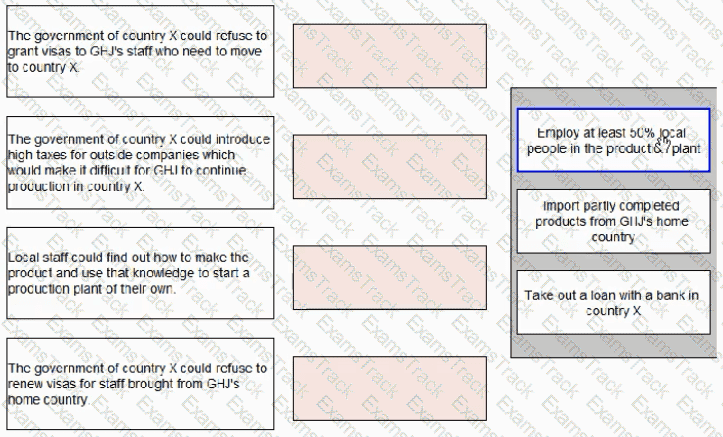
CI IJ has decided to move its production plant to overseas country X. This would make the product cheaper to produce. The technology used to make the product is very advanced and some of the skilled staff would have to move to country X.
The Production Director has identified that there are some political risks in moving to county X.
For each of the political risks of moving to country X shown below, select the correct method for reducing the risk.
Which of the following statements about the tax impact on debt finance is correct?
A company is currently all-equity financed with a cost of equity of 9%.
It plans to raise debt with a pre-tax cost of 3% in order to buy back equity shares.
After the buy-back, the debt-to-equity ratio at market values will be 1 to 2.
The corporate income tax rate is 25%.
Which of the following represents the company's cost of equity after the buy-back according to Modigliani and Miller's Theory of Capital Structure with taxes?
NNN is a company financed by both equity and debt. The directors of NNN wish to calculate a valuation of the company's equity and at a recent board meeting discussed various methods of business valuation.
Which THREE of the following are appropriate methods for the directors of NNN to use in this instance?
|
PDF + Testing Engine
|
|---|
|
$74.7 |
|
Testing Engine
|
|---|
|
$67.5 |
|
PDF (Q&A)
|
|---|
|
$59.7 |
CIMA Free Exams |
|---|

|