The financial assistant of a geared company has prepared the following calculation of the company's equity value:
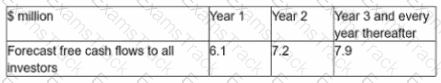
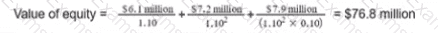
Useful information;
• Tax rate - 20%
• Cost of equity = 12%
• Weighted average cost of capital (WACC)« 10%
" Debt finance of the company comprises a $6 million 7% undated bond trading at par Valuation workings.
Which of the following errors has been made by the financial assistant?
A company which is forecast to experience a strong growth in its profitability is evaluating a potential bond issue.
Which of the following changes in corporate income tax and in bond yields would make the bond issue more attractive to the company?
A company is considering taking out $10.000,000 of floating rate bank borrowings to finance a new project. The current rate available to the company on floating rate barrowings is 8%. The borrowings contain a covenant based on an interested cover of 5 times.
The project is expected to generate the following results:

At what interest rate on the floating rate borrowings is the bank covenant first breached?
Two listed companies in the same industry are joining together through a merger.
What are the likely outcomes that will occur after the merger has happened?
Select ALL that apply.
Which of the following statements are true with regard to interest rate swaps?
Select ALL that apply.
A listed company in a high technology industry has decided to value its intellectual capital using the Calculated Intangible Value method (CIV).
Relevant data for the company:
• Pays corporate income tax at 30%
• Cost of equity is 9%, pre-tax cost of debt is 7% and the WACC is 8%
• The value spread has been calculated as $26 million
Calculate the CIV for the company.
A company has accumulated a significant amount of excess cash which is not required for investment for the foreseeable future.
It is currently on deposit, earning negligible returns.
The Board of Directors is considering returning this excess cash to shareholders using a share repurchase programme.
The majority of shareholders are individuals with small shareholdings.
Which THREE of the following are advantages of the company undertaking a share repurchase programme?
|
PDF + Testing Engine
|
|---|
|
$74.7 |
|
Testing Engine
|
|---|
|
$67.5 |
|
PDF (Q&A)
|
|---|
|
$59.7 |
CIMA Free Exams |
|---|

|