John visits an online shop that stores the IDs and prices of the items to buy in a cookie. After selecting the items that he wants to buy, the attacker changes the price of the item to 1. Original cookie values: ItemID1=2 ItemPrice1=900 ItemID2=1 ItemPrice2=200 Modified cookie values: ItemID1=2 ItemPrice1=1 ItemID2=1 ItemPrice2=1 Now, he clicks the Buy button, and the prices are sent to the server that calculates the total price. Which of the following hacking techniques is John performing?
Cross site scripting
Man-in-the-middle attack
Cookie poisoning
Computer-based social engineering
John is performing cookie poisoning. In cookie poisoning, an attacker modifies the value of cookies before sending them back to the server. On modifying the cookie values, an attacker can log in to any other user account and can perform identity theft. The following figure explains how cookie poisoning occurs:
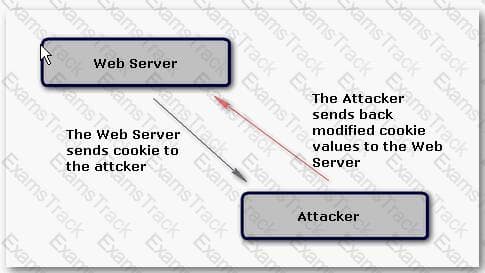 C:\Documents and Settings\user-nwz\Desktop\1.JPG
C:\Documents and Settings\user-nwz\Desktop\1.JPG
For example: The attacker visits an online shop that stores the IDs and prices of the items to buy in a cookie. After selecting the items that he wants to buy, the attacker changes the price of the item to 1. Original cookie values: ItemID1= 2 ItemPrice1=900 ItemID2=1 ItemPrice2=200 Modified cookie values: ItemID1= 2 ItemPrice1=1 ItemID2=1 ItemPrice2=1 Now, the attacker clicks the Buy button and the prices are sent to the server that calculates the total price. Another use of a Cookie Poisoning attack is to pretend to be another user after changing the username in the cookie values: Original cookie values: LoggedIn= True Username = Mark Modified cookie values: LoggedIn= True Username = Admin Now, after modifying the cookie values, the attacker can do the admin login.
Answer: A is incorrect. A cross site scripting attack is one in which an attacker enters malicious data into a Website. For example, the attacker posts a message that contains malicious code to any newsgroup site. When another user views this message, the browser interprets this code and executes it and, as a result, the attacker is able to take control of the user's system. Cross site scripting attacks require the execution of client-side languages such as JavaScript, Java, VBScript, ActiveX, Flash, etc. within a user's Web environment. With the help of a cross site scripting attack, the attacker can perform cookie stealing, sessions hijacking, etc.
You work as a Network Auditor for XYZ CORP. The company has a Windows-based network. While auditing the company's network, you are facing problems in searching the faults and other entities that belong to it. Which of the following risks may occur due to the existence of these problems?
Residual risk
Inherent risk
Secondary risk
Detection risk
Detection risks are the risks that an auditor will not be able to find what they are looking to detect. Hence, it becomes tedious to report negative results when material conditions (faults) actually exist. Detection risk includes two types of risk: Sampling risk: This risk occurs when an auditor falsely accepts or erroneously rejects an audit sample. Nonsampling risk: This risk occurs when an auditor fails to detect a condition because of not applying the appropriate procedure or using procedures inconsistent with the audit objectives (detection faults). Answer: A is incorrect. Residual risk is the risk or danger of an action or an event, a method or a (technical) process that, although being abreast with science, still conceives these dangers, even if all theoretically possible safety measures would be applied (scientifically conceivable measures). The formula to calculate residual risk is (inherent risk) x (control risk) where inherent risk is (threats vulnerability). In the economic context, residual means "the quantity left over at the end of a process; a remainder". Answer: B is incorrect. Inherent risk, in auditing, is the risk that the account or section being audited is materially misstated without considering internal controls due to error or fraud. The assessment of inherent risk depends on the professional judgment of the auditor, and it is done after assessing the business environment of the entity being audited. Answer: C is incorrect. A secondary risk is a risk that arises as a straight consequence of implementing a risk response. The secondary risk is an outcome of dealing with the original risk. Secondary risks are not as rigorous or important as primary risks, but can turn out to be so if not estimated and planned properly.
Which of the following encryption encoding techniques is used in the basic authentication method?
HMAC_MD5
Md5
DES (ECB mode)
Base64
Base64 encryption encoding, which can easily be decoded, is used in the basic authentication method. Answer: B is incorrect. The Md5 hashing technique is used in the digest authentication method. Answer: A is incorrect. The HMAC_MD5 hashing technique is used in the NTLMv2 authentication method. Answer: C is incorrect. DES (ECB mode) is used in the NTLMv1 authentication method.
Which of the following are HTML tags, used to create a table?
tags. The
|
