An organization has implemented the cluster with two customer hosted Mule runtimes is hosting an application.
This application has a flow with a JMS listener configured to consume messages from a queue destination. As an integration architect can you advise which JMS listener configuration must be used to receive messages in all the nodes of the cluster?
Refer to the exhibit.
A Mule application is deployed to a multi-node Mule runtime cluster. The Mule application uses the competing consumer pattern among its cluster replicas to receive JMS messages from a JMS queue. To process each received JMS message, the following steps are performed in a flow:
Step l: The JMS Correlation ID header is read from the received JMS message.
Step 2: The Mule application invokes an idempotent SOAP webservice over HTTPS, passing the JMS Correlation ID as one parameter in the SOAP request.
Step 3: The response from the SOAP webservice also returns the same JMS Correlation ID.
Step 4: The JMS Correlation ID received from the SOAP webservice is validated to be identical to the JMS Correlation ID received in Step 1.
Step 5: The Mule application creates a response JMS message, setting the JMS Correlation ID message header to the validated JMS Correlation ID and publishes that message to a response JMS queue.
Where should the Mule application store the JMS Correlation ID values received in Step 1 and Step 3 so that the validation in Step 4 can be performed, while also making the overall Mule application highly available, fault-tolerant, performant, and maintainable?
An external web UI application currently accepts occasional HTTP requests from client web browsers to change (insert, update, or delete) inventory pricing information in an inventory system's database. Each inventory pricing change must be transformed and then synchronized with multiple customer experience systems in near real-time (in under 10 seconds). New customer experience systems are expected to be added in the future.
The database is used heavily and limits the number of SELECT queries that can be made to the database to 10 requests per hour per user.
What is the most scalable, idiomatic (used for its intended purpose), decoupled. reusable, and maintainable integration mechanism available to synchronize each inventory pricing change with the various customer experience systems in near real-time?
Refer to the exhibit.
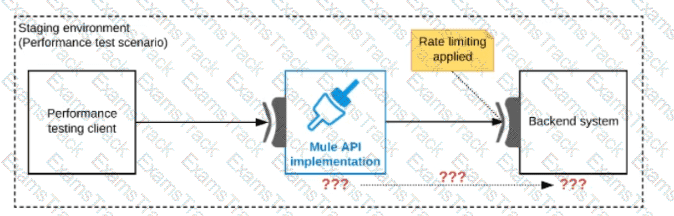
One of the backend systems invoked by an API implementation enforces rate limits on the number of requests a particular client can make. Both the backend system and the API implementation are deployed to several non-production environments in addition to production.
Rate limiting of the backend system applies to all non-production environments. The production environment, however, does NOT have any rate limiting.
What is the most effective approach to conduct performance tests of the API implementation in a staging (non-production) environment?
An organization has decided on a cloudhub migration strategy that aims to minimize the organizations own IT resources. Currently, the organizational has all of its Mule applications running on its own premises and uses an premises load balancer that exposes all APIs under the base URL https://api.acme.com
As part of the migration strategy, the organization plans to migrate all of its Mule applications and load balancer to cloudhub
What is the most straight-forward and cost effective approach to the Mule applications deployment and load balancing that preserves the public URLs?
A bank is implementing a REST API in a Mule application to receive an array of accounts from an online banking platform user interface (UI),retrieve account balances for those accounts from a backend Finance system, and then return the account balances so they can be displayed inthe online banking platform UI. As part of the processing, the MuleSoft API also needs to insert the retrieved account data into an AuditDatabase for auditing purposes. the auditing process should not add latency to the account balance retrieval response back to the onlinebanking platform UI.
The retrieveBalances flow in the Mule application is designed to use an operation in a connector to the Finance system (the Finance operation) that
can only look up one account record at a time, and a operation from a different connector to the Audit system (the Audit operation) that can only
insert one account record at a time.
To best meet the performance-related requirements, what scope or scopes should be used and how should they be used to incorporate the Finance
operation and Audit operation into the retrieveBalances flow?
According to MuleSoft, which deployment characteristic applies to a microservices application architecture?
A company is implementing a new Mule application that supports a set of critical functions driven by a rest API enabled, claims payment rules engine hosted on oracle ERP. As designed the mule application requires many data transformation operations as it performs its batch processing logic.
The company wants to leverage and reuse as many of its existing java-based capabilities (classes, objects, data model etc.) as possible
What approach should be considered when implementing required data mappings and transformations between Mule application and Oracle ERP in the new Mule application?
An application load balancer routes requests to a RESTful web API secured by Anypoint Flex Gateway.
Which protocol is involved in the communication between the load balancer and the Gateway?
According to MuleSoft, what Action should an IT organization take regarding its technology assets in order to close the IT delivery.
|
PDF + Testing Engine
|
|---|
|
$49.5 |
|
Testing Engine
|
|---|
|
$37.5 |
|
PDF (Q&A)
|
|---|
|
$31.5 |
Salesforce Free Exams |
|---|

|