A company has configured an organization in AWS Organizations for its AWS accounts. AWS CloudTrail is enabled in all AWS Regions.
A security engineer must implement a solution to prevent CloudTrail from being disabled.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A company runs a global ecommerce website that is hosted on AWS. The company uses Amazon CloudFront to serve content to its user base. The company wants to block inbound traffic from a specific set of countries to comply with recent data regulation policies.
Which solution will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
A company wants to establish separate AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) keys to use for different AWS services. The company's security engineer created the following key policy to allow the infrastructure deployment team to create encrypted Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volumes by assuming the InfrastructureDeployment IAM role:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "key-policy-ebs",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Enable IAM User Permissions",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:root"
},
"Action": "kms:*",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "Allow use of the key",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/aws-reserved/sso.amazonaws.com/InfrastructureDeployment"
},
"Action": [
"kms:Encrypt",
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:ReEncrypt*",
"kms:GenerateDataKey*",
"kms:DescribeKey",
"kms:CreateGrant",
"kms:ListGrants",
"kms:RevokeGrant"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"kms:ViaService": "ec2.us-west-2.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}
The security engineer recently discovered that IAM roles other than the InfrastructureDeployment role used this key for other services.
Which change to the policy should the security engineer make to resolve these issues?
A security engineer has designed a VPC to segment private traffic from public traffic. The VPC includes two Availability Zones. The security engineer has provisioned each Availability Zone with one private subnet and one public subnet. The security engineer has created three route tables for use with the environment. One route table is for the public subnets, and two route tables are for the private subnets (one route table for the private subnet in each Availability Zone).
The security engineer discovers that all four subnets are attempting to route traffic out through the internet gateway that is attached to the VPC.
Which combination of steps should the security engineer take to remediate this scenario? (Select TWO.)
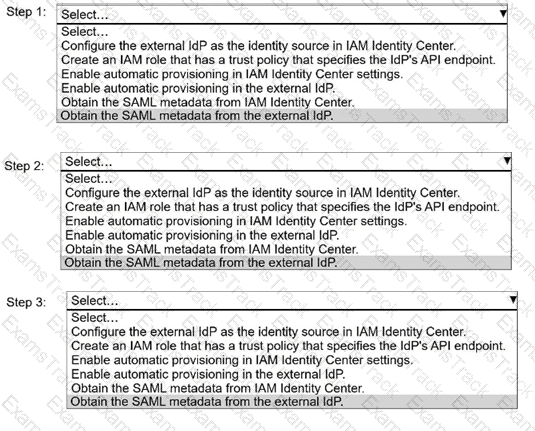
A security engineer needs to implement AWS IAM Identity Center with an external identity provider (IdP).
Select and order the correct steps from the following list to meet this requirement. Select each step one time or not at all. (Select and order THREE.)
. Configure the external IdP as the identity source in IAM Identity Center.
. Create an IAM role that has a trust policy that specifies the IdP's API endpoint.
. Enable automatic provisioning in IAM Identity Center settings.
. Enable automatic provisioning in the external IdP.
. Obtain the SAML metadata from IAM Identity Center.
. Obtain the SAML metadata from the external IdP.
A company is running an application in the eu-west-1 Region. The application uses an AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) customer managed key to encrypt sensitive data. The company plans to deploy the application in the eu-north-1 Region. A security engineer needs to implement a key management solution for the application deployment in the new Region. The security engineer must minimize changes to the application code.
Which change should the security engineer make to the AWS KMS configuration to meet these requirements?
A company uses AWS to run a web application that manages ticket sales in several countries. The company recently migrated the application to an architecture that includes Amazon API Gateway, AWS Lambda, and Amazon Aurora Serverless. The company needs the application to comply with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) v4.0. A security engineer must generate a report that shows the effectiveness of the PCI DSS v4.0 controls that apply to the application. The company's compliance team must be able to add manual evidence to the report.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company detects bot activity targeting Amazon Cognito user pool endpoints. The solution must block malicious requests while maintaining access for legitimate users.
Which solution meets these requirements?
A company is planning to deploy a new log analysis environment. The company needs to analyze logs from multiple AWS services in near real time. The solution must provide the ability to search the logs and must send alerts to an existing Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic when specific logs match detection rules.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company needs to identify the root cause of security findings and investigate IAM roles involved in those findings. The company has enabled VPC Flow Logs, Amazon GuardDuty, and AWS CloudTrail.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
|
PDF + Testing Engine
|
|---|
|
$49.5 |
|
Testing Engine
|
|---|
|
$37.5 |
|
PDF (Q&A)
|
|---|
|
$31.5 |
Amazon Web Services Free Exams |
|---|

|